
2-tier ERP strategy and cloud ERP
The 2-tier ERP strategy offers companies a flexible way of managing global business processes centrally while meeting local requirements in a targeted manner. The use of cloud ERP in particular creates new opportunities to reduce costs, optimize scalability and drive digital transformation.
Find out in this article why companies rely on the 2-tier strategy, what advantages it offers and in which use cases it is particularly useful.
What is a 2-tier ERP strategy?
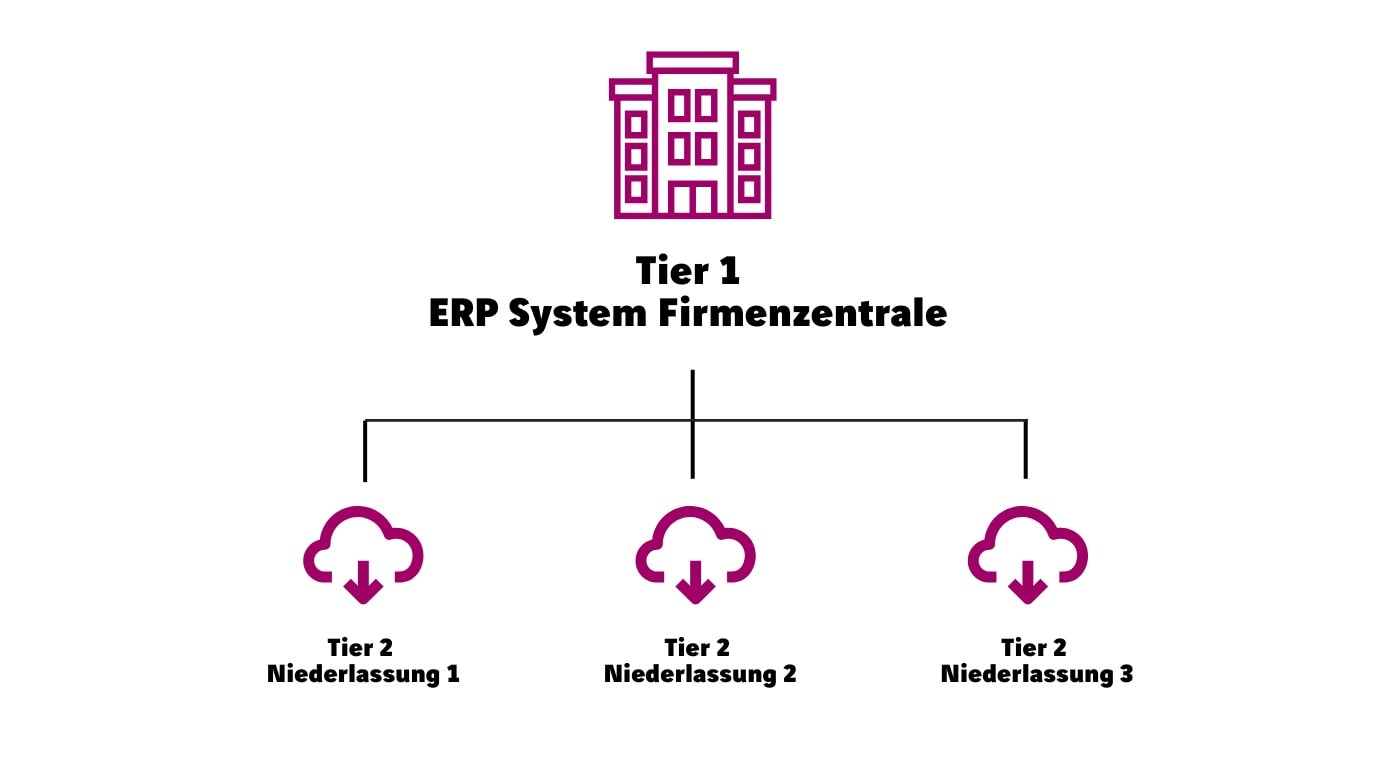
A 2-tier ERP strategy refers to the implementation of two tiers of different ERP systems:
Tier 1: A central ERP system that supports all business processes and can be correspondingly complex.
Tier 2: A largely standardized system to be rolled out globally, which provides all the necessary processes for regional branches or subsidiaries. Customization remains minimal in this system and is usually limited to local legal requirements.
In contrast to the 1-tier ERP strategy, which relies on a single overarching system, the 2-tier ERP strategy allows processes to be simplified while at the same time standardizing basic procedures.

Why do companies opt for a 2-tier strategy?
Companies choose the 2-tier ERP strategy to bring all branches onto one site more quickly. This makes rollouts more efficient, reporting more consistent, onboarding new employees faster and optimizes processes in general. Here are some of the key business reasons:
Faster implementations: New branches or markets become operational more quickly because Tier 2 ERP systems can be set up much faster than Tier 1 solutions.
Adaptation to local requirements: Many companies have to comply with a large number of regional regulations, tax laws or currency specifics. However, these should only be mapped in the local branches where they are necessary. These local adaptations can be covered by SAP S/4HANA Public Cloud. The solution is a complex, central core system with simple systems for the local branches.
Flexibility for subsidiaries: Local business units can react more agilely to market conditions with a Tier 2 system and test and validate new business models without influencing sister companies too early.
Cost efficiency: Instead of the high costs of customizing a comprehensive Tier 1 system, companies are opting for economical standard solutions for Tier 2 applications.
Typical use cases for the 2-tier ERP strategy
The 2-tier ERP strategy is particularly suitable for complex, globally active companies with diverse structures. Here are some typical use cases:
- Pilot projects for digital transformation
Companies that want to test digital innovations often use Tier 2 systems to carry out projects in individual units before scaling them up on a global level. - Expansion into new markets
When companies expand into new countries, they often face regulatory and cultural differences. A Tier 2 ERP system allows local units to be equipped with the right functions quickly and cost-effectively. - Industry-specific business units
Individual departments or subsidiaries that operate in specialized markets often require specific ERP functions. For example, production sites require different functions than a distribution center. - Business units depending on day-to-day business
Smaller branches or subsidiaries often have neither the resources nor the need for a comprehensive Tier 1 system. Lean, cost-effective tier 2 solutions can make sense here. - Processing smaller business units
Smaller branches or subsidiaries often have neither the resources nor the need for a comprehensive Tier 1 system. Lean, cost-effective tier 2 solutions can make sense here. - Pilot projects for digital transformation
Companies that want to test digital innovations often use Tier 2 systems to carry out projects in individual units before scaling them up on a global level.
Cloud ERP systems are revolutionizing the 2-tier ERP strategy approach. As a web-based Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) model, they offer considerable advantages, especially for tier 2 systems, which have a direct impact on business processes.
Advantages of cloud ERP
- Cost efficiency
The subscription-based model eliminates the need for high investments in IT infrastructure. This makes cloud ERP particularly attractive for smaller business units or subsidiaries. - Rapid deployment
Cloud ERP systems can be implemented quickly, making it easier to enter new markets or regions. - Scalability
Companies can flexibly adapt their cloud capacities and user licenses to growing requirements or seasonal fluctuations. - Flexibility and mobility
Employees worldwide can access cloud ERP via the internet, supporting mobile work processes and international teams. - Automatic updates
Cloud ERP solutions automatically keep systems up to date with regular updates, which relieves the IT department and allows innovations to be implemented quickly.
The challenges of cloud ERP
- Data security and compliance
Companies must ensure that providers comply with strict security and data protection guidelines (e.g. GDPR). SAP delivers the highest standards here in the form of a data protection management system. - Dependence on the internet connection
A reliable and powerful network connection is essential for smooth operation. SAP also offers offline modes as required for vulnerable use cases, such as mobile applications. - Integration with central Tier 1 systems
It is crucial that cloud and on-premise systems work together seamlessly to efficiently meet both global and local requirements. With SAP BTP as a stable middleware, this is possible.
Success stories from the field
- Global companies such as Siemens, Amazon and Unilever have successfully implemented the 2-tier ERP strategy in their business models. Siemens uses a combination of a powerful on-premise tier 1 system for its headquarters and cloud ERP solutions for subsidiaries. This has both reduced operating costs and shortened time to market. Unilever uses flexible cloud ERP systems to meet regional requirements while integrating innovative data analytics directly into the central platform.
However, the 2-tier ERP strategy can also be a sensible approach for medium-sized companies with sales companies abroad in order to optimize their processes cost-efficiently in all companies with a cloud ERP that is introduced more quickly.
Conclusion – The future of business software
The combination of a 2-tier ERP strategy and cloud ERP is a powerful concept in the context of digital transformation. This strategy enables companies to map their business processes in a flexible core system.
With the right planning and a competent implementation partner, companies can take advantage of cloud ERP to reduce costs, increase scalability and at the same time promote collaboration between global and local teams. With the 2-tier ERP strategy, companies have a clear cost saving in long-term ERP support, reporting and rolling out new features and innovations – because everyone gets the same thing.
Companies looking for both innovation and stability will find the 2-tier ERP strategy a key to success.
Curious?
Get in touch with our experienced SAP transformation experts now!

Felix Sander
Head of Consulting Germany
This could also be of interest to you

SAP Solutions & Operations
SAP S/4HANA financial accounting for G. Englmayer

SAP Solutions & Operations

